The need to manage waste and its valuation raises the opportunity for promising environmental projects, like FUELCAM, by the Universidad Politécnica de Madrid and the Universidad de Castilla la Mancha, focused on the use of hydrogenated terpenes to create biofuel from orange peels or pine tree resin.
“This project originated five years ago to revalorize waste in the Castilla La Mancha region”, explains Magín Lapuerta, a professor at the Universidad de Castilla – La Mancha, where he coordinates the Grupo de Combustibles y Motores (GCM-UCLM) and assesses the Committee for the European norms on fuel.
“The first part of this job involved working with turpentine, a terpene distilled from pine tree resin, that is after subject to hydrogenation, so that it won’t produce black smoke at combustion”, explains Lapuerta.
Then, it was the turn for orange peels, a readily available material since it is a byproduct that is not used by coopearatives and farmers.
This project stems from David Donoso’s thesis. David is a researcher at the ETS de Ingeniería Industrial de la UCLM, that comprises three research lines with three different raw materials, the three of them terpenos hidrogenados: turpentine, hydrogenated orange oil and CST, which is sulfate turpentine, a paper industry byproduct.
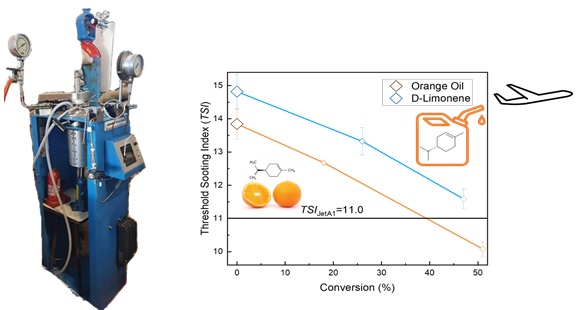
“Our research confirms that fully hydrogenating fuel allows to reduce soot by 55%”, says David Donoso.
Turpentine isn’t really a byproduct. It’s extracted from pine trees, and it’s mainly used to produce substances like turpentine spirits. While its extraction would have major impact on the pine tree industry and have applications to prevent fires, this research line doesn’t show much promise.
For that reason, they focused on CST and orange peels. “The research to create fuel was done with a reactor at the Universidad Politécnica de Madrid. We created enough to burn it with an engine”, explains Lapuerta.
The fuel was tested at Castilla La Mancha mixed with diesel fuel. In the test formulas, 20% is hydogenated turpentine or hydrogenated orange oil, and 80% is diesel.
“The percentage of biofuel could be raised. We give added value with the hydrogenation”, researchers say. It could also be tested in gas engines.
“Now we need to take the leap on an industrial scale, by testing biofuels mixed with JetA1 in aircraft turbines”, explains José Laureano Canoira López, professor at the Chemical engineering area of the Universidad Politécnica de Madrid (UPM).
“We still need to find turbines to test out these results in the aviation industry. We need a refinery or biorefinery company willing to hydrogenate the materials for us and prepare a large amount to start testing on real planes”, researchers say.
However, there is a major gap that seems tough to close. In order to test out efficiently they would need to produce at least 100 liters, but for fuel companies to find the operation profitable, they would need to produce at least 1,000 liters and take the risk.
The ASTM (American Society for Testing and Materials) lays down the possibility of using from 10% to 50% of biofuels in aviation, as long as they meet the requirements.
There are other research lines with potential. There are other types of terpene waste, such as biowaste from parks and gardens maintenance, mostly leaves, which could also be used to make biofuels.
